Notebook
Notebook is a web-based code editor that can be used for writing code and viewing the results of interactive data analysis. This article introduces the basics of how to use Notebook within the product, including how to navigate the toolbar and how to perform various cell operations.
Creating a Notebook
Click on the sidebar: Analysis -> New Notebook
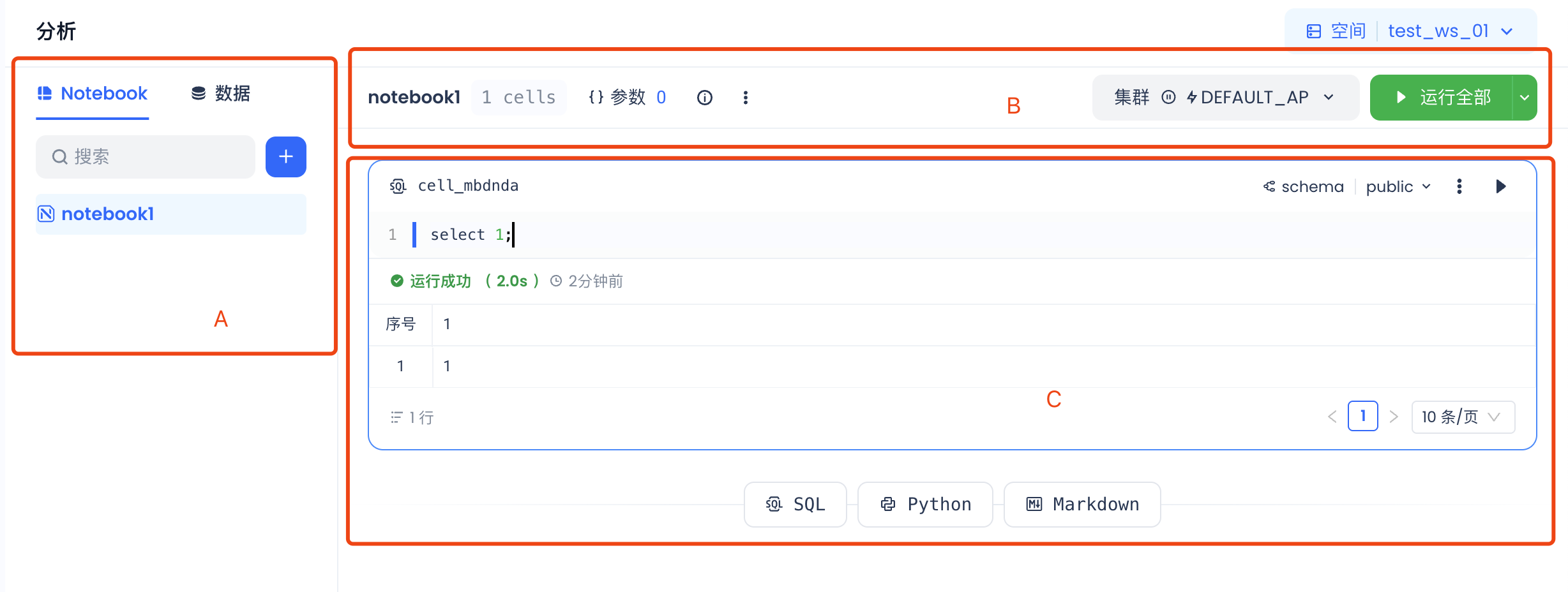
A: Left sidebar Directory Tree and Data Tree B: Notebook Function Operations Area C: Notebook Cells
Left Sidebar Directory Tree and Data Tree
- Notebook: The Directory Tree is used to manage the task code of Notebooks under the current workspace in an orderly manner. Creating folders is currently not supported.
- Data: Below the Notebook section, the data directory tree for all data in the user's Region is displayed, presented hierarchically as Workspace -> Schema -> Table/View.
Function Operations Area
| 序号 | 图标 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | The global parameters of the current Notebook. If custom parameters are referenced below in the format ${custom_parameter}, users need to input the parameter values here.Note: Parameters are global. If the same custom parameter name is referenced in different cells, it will be replaced with the same parameter value during execution. |
| 2 |   | Run All Cells or Stop Execution." The name of this button changes dynamically based on the notebook's status. After the user clicks "Run All", the cells will be executed sequentially in order. |
| 3 |  | Cluster information for executing SQL cells. |
| 4 |  | More Actions: Supports renaming, duplicating, and deleting the Notebook. |
Notebook Cells
Creating a Cell
After creating a new Notebook task, click on different unit types in the operations area to create specific unit cells.

Cell Types
Notebook contains two types of cell collections: Code cells and Markdown cells.
Code Cells Code cells contain executable code, supporting:
- SQL Cell: Executes ClickZetta SQL queries. If an SQL cell is selected, the user needs to choose the specific Schema information of the Yunqi data they want to access. After filtering, in this unit cell, users can directly input table names, and the system will auto-complete the specific three-part identifier code based on the Schema and current workspace information.
- Python Cell: Executes Python data analysis code.
- Markdown Cells: Markdown cells contain Markdown code that is rendered as text and graphics. Use Markdown to document or explain your code. You can add or delete any type of cell in the Notebook to organize your work.
Limitation: The output size of a cell is limited to a maximum of 10MB.
Cell Operations
| 序号 | 图标 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 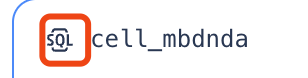 | Cell Types.Different cell types support different languages. |
| 2 |  | Cell Name. When a user creates a new cell, the system automatically assigns a default cell name. Double-clicking this area allows the user to rename the cell.Notebook enables users to directly reference a cell's output values in Python scripts. This requires users to specify the exact name of the cell containing the output information for data positioning.Cell names only support English letters (both uppercase and lowercase), numbers, and underscores (_). |
| 3 | 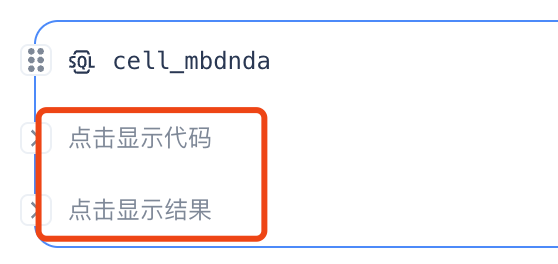 | Expand/Collapse Cell Code and Display Results.When the code content in the current Notebook is too long, users can click the arrow on the left side to separately expand or collapse the code and result areas. |
| 4 |  | Moving Cells. The execution in a Notebook follows a strict sequential order. If users need to adjust the position of a cell, they can hover the mouse over the cell, select the move handle area, and then drag the cell up or down to reposition it. |
| 5 |  | Quickly Add Cells.When hovering over the area above or below the central region of the current cell, new cells can be quickly added above or below the current position. |
| 6 |  | run cell。 |
| 7 |  | More Cell Operations。Rename:Click to assign a new name to the cell。Clear Output: Clears the execution results of the current cell. If other cells depend on the output of this cell, their execution may fail。Delete: Deletes the cell. |
Running Cells
Basic Operations
To run a code cell, click the run button in the upper left corner of the code cell, or click "Run All" in the upper left corner of the entire Notebook area.
- Run Single: Only runs the current cell. If the current cell references the output of other cells, please ensure those cells have been successfully run. The execution time should not exceed 30 minutes. If it exceeds 30 minutes, pod clearing scenarios may occur.
- Run All: After clicking, cells are executed sequentially from top to bottom. If one cell fails to execute or is paused, all cells below it will be blocked from execution, meaning the status of all cells below will change to "Paused".
Context Communication Between Cells
Yunqi Notebook uses a communication mechanism based on cell naming. Each cell has a unique name (e.g., cell1, cell2, etc.), which can be directly referenced in other cells.
- SQL Cell Output: For multi-segment SQL, only the last segment serves as the output of that cell.
- Direct Referencing: The result of an SQL cell can be directly used as a pandas DataFrame.
- No Conversion Needed: No additional operations like
to_pandas()are required. - Referencing by Name: Access results directly via the cell name.
